I heard of a father who was visiting
one of his adult children. He was asked by the child to go out and get
something out of his son's car. The father went to a similar car
of the same color and make. The son later asked his Mother, "Does Dad
have Alzheimer's? "
Improving Memory Articles
Many brain regions are involved in this process. For example, the cerebral cortex — the large outer layer of the brain — acquires new information as input from our senses. The amygdala tags information as being worthy of storage. Nearby, the hippocampus stores memories. And the frontal lobes help us consciously retrieve information.
The aging memory
Many people notice a difference in memory starting in their 50s. That's when age-related chemical and structural changes can begin in brain regions involved with memory processing, such as the hippocampus or the frontal lobes. These changes may slow processing speed, making it hard to recall familiar names or words.Other factors may be at play as well. "Working memory — a mental scratch pad that allows us to use important information throughout the day — is susceptible to depression, anxiety, and stress," explains Dr. Salinas, "and a lack of sleep can affect the brain's retention and use of information."
A medication side effect may also affect memory. For example, if you use an anti-anxiety drug like clonazepam (Klonopin), its sedating side effects can make your brain less alert and more sluggish. This in turn makes it more challenging for your brain to carry out the essential encoding, recording, and retrieval steps of memory.
Dr. Salinas says addressing these problems first often helps improve memory.
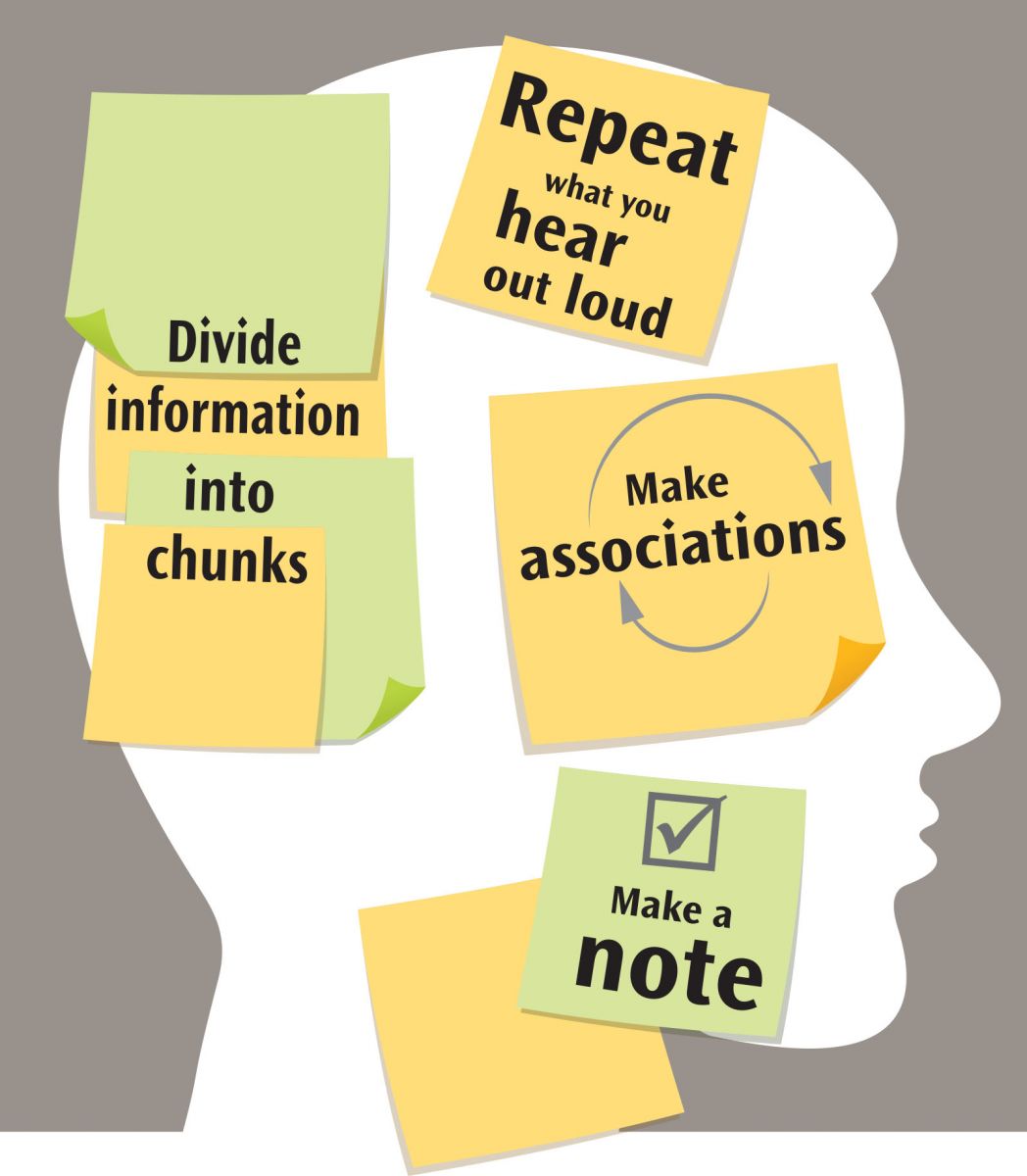
Memory tricks
1. Repeat what you hear out loud, such as someone's name, or an address, or a new idea. Repetition increases the likelihood you'll record the information and be able to retrieve it later. "With each repetition, your brain has another opportunity to encode the information," explains Dr. Salinas. "The connections between brain cells are reinforced, much like blazing a trail in the woods. The more you walk the same trail, the easier it is to walk it the next time."
2. Make a note of people you need to call, errands to run, and appointments. "We are much better at recognition than recall," Dr. Salinas explains. "With recognition, such as reading a list, you have additional hooks or hints that help you find the information you're looking for."
3. Make associations between old and new information. Connect a person's first name to something familiar. For example, if the person's name is Sandy, imagine that person on a beach. Or create a story around a shopping list. "Our brain is good at sequences, and putting things into a story helps. The more ridiculous, the more memorable it is. For example, if your list is milk, eggs, and bread, the story could be that you are having milk with Elvis over an egg sandwich," Dr. Salinas suggests.
4. Divide information into chunks, such as taking a long number and remembering it more like a phone number. "It's hard to store a long number," says Dr. Salinas, "but easier to store little bits through working memory." If you're trying to memorize a speech for a wedding toast, focus on getting only one sentence or idea down at a time, not the whole speech in one take.
www.health.harvard.edu/aging/4-tricks-to-rev-up-your-memory

If you would like to read our book, please go to or get our book on Kindle please go to
https://www.amazon.com/Broken-Minds-Healing-Youre-Losing/dp/0825421187/ref=tmm_pap_swatch_0?_encoding=UTF8&qid=&sr=
: If you would like a sale price for our book, please see our web-site.
http://heartfeltmin.org/resources.html
.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Please feel free to respond to my blog. I value your opinion.